- GET CORRECTLY DIAGNOSED NOW - WORLD CLASS EMG TESTING
- 312-877-0035
EMG Best Test To Diagnose Neuropathy
Best Test to Diagnose Neuropathy is the EMG/NCV Nerve Test
Exams and Tests for Neuropathy Symptoms
How Your Doctor Properly Diagnose Neuropathy
To diagnose Neuropathy correctly and develop a list of possible causes, an EMG/NCV (Electromyography/Nerve Conduction Velocity Study) is the most accurate and correct test and is required for a Confirmation Diagnosis.
The EMG Test measures:
1) Your nerves speed
2) Amount of electricity moving through the nerve
3) Reaction time of the nerve to stimulus
4) Overall pattern of peripheral nervous system function
5) Level of Severity! Is it progressively Worse?
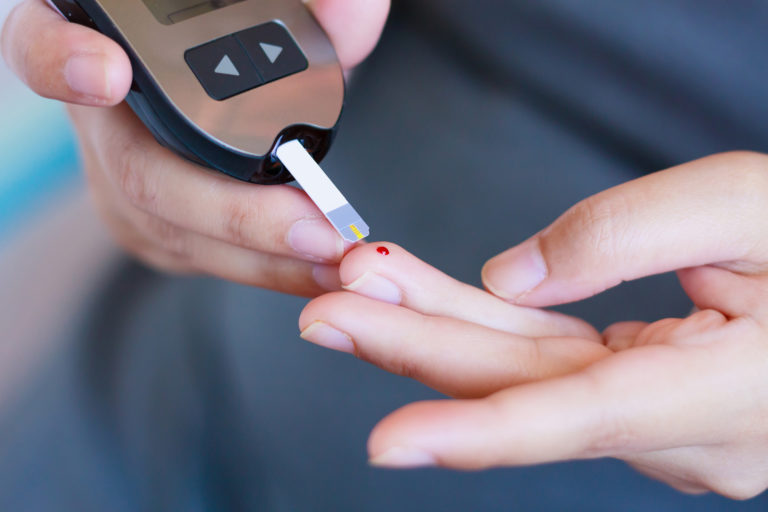
What Causes Neuropathy?
Diabetes is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy in the US.
Neuropathy can also be caused by other health conditions and certain medications. In some cases, no cause can be identified and this is termed idiopathic neuropathy. Diabetes Peripheral neuropathy caused by either type 1 diabetes (Juvenile Onset) or type 2 diabetes (Adult Onset) is called diabetic polyneuropathy. It's probably caused by high levels of glucose in your blood damaging the tiny blood vessels that supply your nerves.Peripheral neuropathy becomes more likely the longer you've had diabetes. Up to one in every four people with the condition experience some pain caused by nerve damage.
If you have diabetes, your risk of polyneuropathy is higher if your blood sugar is poorly controlled or you smoke, regularly consume large amounts of alcohol and/or are over 40 years old
If you have diabetes, you should examine your own feet regularly to check for ulcers (open wounds or sores.
Other Causes
As well as diabetes, there are many other possible causes of peripheral neuropathy.
Some of the health conditions that can cause peripheral neuropathy include:
- Excessive alcohol drinking for years
- Low levels of vitamin B12 or other vitamins
- Physical damage to the nerves; such as from an injury or during surgery
- An underactive thyroid gland(hypothyroidism)
- Specific infections – such as shingles, Lyme disease, diphtheria, botulism and HIV
- Inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis)
- Chronic liver disease or chronic kidney disease
- Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) – the presence of an abnormal protein in the blood
- Certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma (a cancer of the lymphatic system) and multiple myeloma (a type of bone marrow cancer)
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease and other types of hereditary motor sensory neuropathy – genetic conditions that cause nerve damage, particularly in the feet
- High levels of toxins in your body, such as arsenic, lead or mercury
- Guillain-Barré syndrome – a rare condition that causes rapid onset of paralysis within days
- Amyloidosis – a group of rare but serious conditions caused by deposits of abnormal protein called amyloid in tissues and organs throughout the body
- Conditions caused by overactivity of the immune system – such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus or Sjogren's syndrome
Medication
A few medications may sometimes cause peripheral neuropathy as a side effect in some people. These include:
• Several types of chemotherapy for cancer – especially for bowel cancer, lymphoma or myeloma
• Several antibiotics, if taken for months – such as metronidazole or nitrofurantoin
• Phenytoin – used to treat epilepsy – if taken for a long time
• Amiodarone and thalidomide

Confirming if you have a neuropathy
A neurological testing specialist will conduct nerve tests including:
- Nerve Conduction Velocity test (NCV) – where small metal wires called electrodes are placed on your skin which release tiny electric shocks that stimulate your nerves; the speed and strength of the nerve signal is measured
- Electromyography (EMG) – where a small needle is inserted through your skin into your muscle and used to measure the electrical activity of your muscles NCS and EMG are usually carried out at the same time.
Identifying the cause of a neuropathy
Your Family Doctor usually has a good understanding of what is the underlying cause of a peripheral neuropathy. If diabetes is suspected, they can usually make an initial diagnosis based on your symptoms, a physical examination and checking the levels of glucose in your blood and urine. The confirmatory testing is then the EMG/NCV Test.
If you're taking a medication known to cause peripheral neuropathy, your Family Docotr may temporarily stop or reduce your dose to see whether your symptoms improve. Occasionally, a nerve biopsy may be carried out as part of your diagnosis. This is a minor surgical procedure where a small sample of a peripheral nerve is removed from near your ankle so it can be examined under a microscope. It's then checked for changes that could be a sign of certain types of peripheral neuropathy. However, nerve biopsies are rarely needed.
GET RELIEF FROM NEUROPATHY NOW
(312) 877-0035
Fast & Convenient
Expert EMG Neurological Diagnostic Tests - Same Day Testing Available! We ALSO Document work & Personal Injuries for legal cases as well. We have FOUR locations to serve you.